Uterine Fibroids
 The chances are that you aren’t aware you have fibroids, which are also called leiomyomas or myomas. Many women don’t experience any symptoms. Fibroids are essentially small balls of muscle that grow in the muscular wall tissue of your uterus. They’re almost always non-cancerous, rarely turn into cancer in the future.
The chances are that you aren’t aware you have fibroids, which are also called leiomyomas or myomas. Many women don’t experience any symptoms. Fibroids are essentially small balls of muscle that grow in the muscular wall tissue of your uterus. They’re almost always non-cancerous, rarely turn into cancer in the future.
Women who do experience symptoms may communicate any of the following:
- Heavy bleeding or painful periods
- Anemia
- Feeling a sense of fullness in your lower stomach
- Noticing your lower abdomen appears to be distended
- Having to urinate frequently
- Pain during sex
- Lower back pains
- Complications during pregnancy and labor
- Rarely, reproductive problems
There is no proof of what causes uterine fibroids; however, there is a clear link between hormones (estrogen and progesterone) and their impact on uterine fibroids. Furthermore, the condition runs in families, so you’re at greater risk if you have a close family member who experiences fibroids. Other risk factors include race, African American women being more likely to get fibroids, and environmental factors such as birth control use, obesity, and early onset periods. Uterine fibroids should always be evaluated with a thorough consultation and examination by a physician for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
OB Gynecologist of Women’s Health & Wellness offers comprehensive obstetrics and GYN care in NYC for women of all ages. Our ob-gyn clinic provides a full range of gynecology services, from annual check-ups and routine pap smears to Uterine Fibroids treatment and GYN procedures, surgeries performed in our office or the hospital. In addition, our state-of-the-art center for gynecology in Manhattan, is equipped with the latest ob-gyn equipment.
Diagnosing Uterine Fibroids
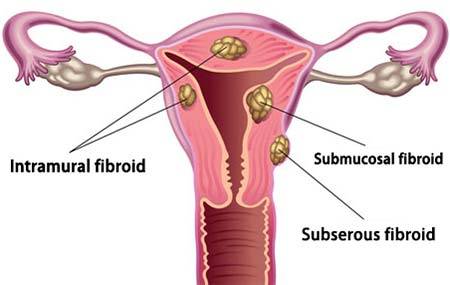
There are several different kinds of fibroids, generally described based on where they develop:
- Submucosal fibroids grow in the uterine cavity.
- Intramural fibroids form in the wall of the uterus.
- Subserosal fibroids occur growing on the outside of the uterus.
Fibroids lead to a larger than the normal uterus. It impacts the size of your uterus just as pregnancy does. Because of this, your NYC OBGYN refers to your uterus size (average size of uterus vs. not) in comparison to a specific number of weeks pregnant. For example, your ob-gyn doctor may tell you that fibroids have put your uterus into the 10-week of pregnancy range, which of course, is more significant than usual. Your gynecologist may also describe your fibroids by comparing them to any of several round objects, from seeds to nuts, a golf ball to a fruit.
Your Midtown Manhattan gynecologist might order some imaging tests to describe a fibroid in greater detail, including:
- Ultrasounds are painless, non-invasive, and can show your ob-gyn doctor or internal pelvic organs.
- Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, uses a magnetic field to produce a detailed picture.
- X-rays are well known and use tiny amounts of radiation to create a picture of solid elements of your body, such as bones.
- Computerized tomography, or CT scan, creates a more three-dimensional image by taking many X-rays and piecing them together.
- Hysterosalpingogram uses injected dye and X-rays to create a picture.
- Sonohysterogram uses injected water and ultrasound to create an image.
- Laparoscopy allows your ob-gyn doctor to see inside your uterus via a small incision in your abdomen. After inserting a thin tube with a light and a camera on its end, your OBGYN can take pictures during this procedure.
- Hysteroscopy also involves a scope on a thin tube with a light. In this procedure, the hysteroscope is inserted through your vagina, past your cervix, and further into your uterus. Polyps can also be detected using this procedure.
Treatment Without Symptoms?
Your doctor will typically treat uterine fibroids only if the symptoms are annoying or painful for you, depending on your gynecologist’s recommendation after careful examination. So usually, your gynecologist either treats your symptoms or removes the fibroids via medications or surgical procedures.
For example, your gynecologist may prescribe medications for fibroids, including:
- Over-the-counter pain medications of your choice, usually nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- As the potential for anemia due to heavy bleeding, iron supplements are a potential hazard with fibroids.
- Low-dose birth control pills containing a combination of hormones that will not stimulate fibroid growth but can slow or stop bleeding
- Birth control injections that are heavy on progesterone, which can provide relief of symptoms
- Hormonal IUDs contain small doses of progesterone-like medicine and can also perform double duty as both birth control and control of symptoms like heavy bleeding.
Surgical solutions for uterine fibroid cysts are rare but include:
- Myomectomy is a procedure that aims at removing fibroids with minimal damage to the healthy uterine tissue surrounding the fibroids. Often, women who would like to get pregnant opt for this procedure. This procedure can be minimal, or it can be major surgery, depending on the location and size of your fibroids.
- Hysterectomy is the removal of your entire uterus. It’s usually only performed when it’s the last solution available to remove fibroids from your reproductive system. It’s a complete and total cure for fibroids, but it means pregnancy is impossible after this surgery. Your doctor will typically retain your ovaries, especially if you’re a younger woman, to keep you from starting menopause too early.
- Endometrial Ablation involves removing or burning out the uterus lining, usually with radiofrequency waves that can reduce how much you bleed and sometimes reduce the amount of pain you have due to problems with the uterus fibroids. This procedure is most favorable for women who have completed childbearing.
- Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) or Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE) cuts off the blood supply to the fibroids using tiny gel particles placed in the fibroids via a small tube threaded through the blood vessels. But, again, this procedure will not allow you to become pregnant later.
Fibroids and Pregnancy
Your doctor may view fibroids as a pregnancy complication because while they don’t typically interfere with getting pregnant, fibroids can cause miscarriage or infertility. There are also concerns that fibroids could raise the risk of certain pregnancy complications.
If you’re trying to get pregnant and you’re aware you have fibroids or have had them in the past, alert your NYC gynecologist to this immediately.
Important Reminder: The only intense of this information is to provide gynecology guidance, not definitive medical advice. Please consult an ob-gyn doctor about your specific condition. Only a trained, experienced gynecologist or certified gynecology NYC specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
Have questions? Schedule an appointment with the best obgyn care provider in Midtown NYC today.
Updated on Sep 23, 2023 by Manhattan Women’s Health and Wellness
Best-in-class
New York Gynecology Clinic
Manhattan Specialty Care in the Press

Call now to make an appointment with our highly rated Manhattan Gynecology doctors regarding your health. We look forward to seeing you!
book online now
(212) 378-9985
New York City Locations:
Manhattan Women's Health & Wellness (Upper East Side)
983 Park Ave, Ste 1D17
New York, NY 10028
(212) 389-1904
Manhattan Women's Health & Wellness (Midtown)
56 W 45th St, Ste 815
New York, NY 10010
(212) 677-7654
Manhattan Women's Health & Wellness (Union Square)
55 W 17th St, Ste 104
New York, NY 10011
(212) 378-9985