Adenomyosis
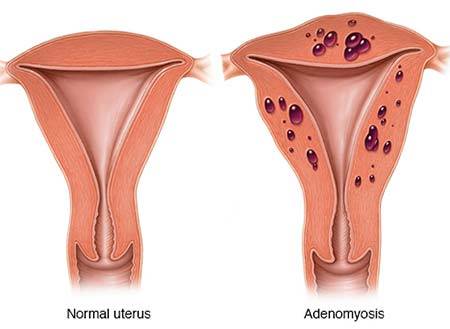 Adenomyosis is a disease that can be difficult to diagnose. The only way for your NYC gynecologist to definitively tell if you have adenomyosis is after you have treated your symptoms with a hysterectomy. The specialist would examine the tissue under a microscope. However, treatment based on ultrasound images or suspicion is usually the best option.
Adenomyosis is a disease that can be difficult to diagnose. The only way for your NYC gynecologist to definitively tell if you have adenomyosis is after you have treated your symptoms with a hysterectomy. The specialist would examine the tissue under a microscope. However, treatment based on ultrasound images or suspicion is usually the best option.
Adenomyosis is a condition that causes the endometrial tissue lining of your uterus to grow into the muscular walls of your uterus. Once the endometrial tissue implants in the uterus muscle, the tissue continues to act as it always does, growing, thickening, breaking up, and bleeding out during your period.
Adenomyosis can be very painful when it causes your uterus to become enlarged. It creates heavy bleeding during your menstrual cycles.
Why It Happens
 The cause of adenomyosis is unknown, but there are theories for this condition. It usually affects women later in life, before menopause, but after they’ve already had kids. It generally improves after you go through menopause because the hormones that cause menstruation are deficient.
The cause of adenomyosis is unknown, but there are theories for this condition. It usually affects women later in life, before menopause, but after they’ve already had kids. It generally improves after you go through menopause because the hormones that cause menstruation are deficient.
Some of the causes of the condition may include:
- Abnormal development in utero, meaning endometrial tissue is deposited outside your uterus while you are still forming in your mother’s womb.
- Tissue that the specialist cuts during another procedure, such as a C-section, may cause invasive growth and instigate the invasion.
- A stem cell-related disease in that bone marrow somehow seeps into the uterus and causes unusual tissue movement.
- Following childbirth, when the uterine lining becomes inflamed. The inflammation may cause a break in the lining of your uterus, which usually forms a natural barrier for the tissue.
No matter how it develops, what is known is that estrogen feeds it. The tissue growth relies on continuing hormone production to fuel its growth, which is why the condition goes away after menopause, where much hormone production reduces.
Symptoms Vary
You may have adenomyosis and not even know it. At other times, the symptoms can be painful and obvious, such as:
- Pain while having sexual intercourse
- Heavy uterine bleeding during your period or periods that last longer than they should
- Strong cramps during your menstrual cycle that get worse as you age
- Sharp, stabbing pain through your pelvis during menstruation
- Passing blood clots with your menstrual blood
Additionally, you may notice a bulging in your abdominal area from where your enlarged uterus protrudes. You might not recognize that it’s your uterus and instead think that your belly has become enlarged and tender. But if you’re experiencing any pain in your abdominal region, it is always a good idea to visit your OBGYN specialists.
Risks Associated with Adenomyosis
Since endometrial tissue needs estrogen to grow, it makes sense that if you’re menopausal or postmenopausal, you’re at a lower risk of developing adenomyosis. Complete understanding of the condition and its start is still under investigation, but recent studies suggest that severe pelvic pain in younger women may originate from adenomyosis. The condition may even appear in women as young as adolescence.
Risk factors that are clear and include:
- Being middle-aged
- Giving birth at least once
- Previous surgery that involved your uteri, such as a Cesarean section or fibroid removal
Additional risk factors related to the condition:
- Adenomyosis with endometriosis makes for a common occurrence. And although these conditions can happen at the same time, endometriosisdoesn’t always cause heavy bleeding.
- Myometrial cyst leads to a rare variant called cystic adenomyosis that repeated hemorrhages might cause in the uterus.
- Adenomyosis and cancer are often linked when you have to take tamoxifen to treat cancer. At the same time, adenomyosis does not necessarily relate to a higher incidence of cancer.
Testing May Prove Helpful
The only way to confirm a diagnosis of adenomyosis is to examine the tissue after you‘ve had a hysterectomy and the doctor has removed your uterus. A hysterectomy can help with pain and bleeding related to adenomyosis; however, this is not the only option. The continual bleeding may not be painful, but it can disrupt your life enormously and lead to anemia with symptoms of depression, feelings of futility, and frustration.
Tests your NYC gynecologist, may order to identify the cause of your excessive bleeding include:
- A pelvic exam, during which he can feel for abnormalities
- A thorough history of your recent bleeding experiences
- Imaging tests such as an MRI and adenomyosis ultrasound to rule out other uterine diseases
- Endometrial biopsy
Treatment Options
Depending on your age, the best solution may be to treat your symptoms to get you to menopause, at which time your adenomyosis will abate.
Effective treatments can include:
- Hormone medicine that combines progestin and estrogen. It may lessen your bleeding. A hormonal IUD, which primarily puts out progestin, also may help reduce your bleeding. Continuous use of oral contraceptives that sometimes eliminate your periods may also provide relief.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen help reduce the discomfort and pain associated with the heavy menstrual cycles you get and relieve some of the heavy bleedings. At the same time, you wait for natural menopause to take place. Many of the treatments women with heavy menstrual cycles use may provide you with some relief as well. Soaking in a warm bath may ease your discomfort, as can putting a heating pad on your abdomen when you have cramps.
- A hysterectomy is a form of definitive symptom management if they’ve become unmanageable and you’re years away from menopause. You only need a partial hysterectomy and can keep your ovaries. Without your uterus, however, you will not be able to get pregnant.
- Endometrial Ablation can help reduce the amount of bleeding you experience during your menses and may even reduce pain associated with periods. This procedure only takes a few minutes and is done in a gynecology office.
All signs and symptoms should always be evaluated with a thorough consultation and examination by a physician for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Have questions about Adenomyosis treatments or diagnosis? Schedule an appointment with the top-rated adenomyosis specialist in NYC, gynecologist today.
Updated on Sep 23, 2023 by Manhattan Women’s Health and Wellness
Best-in-class
New York Gynecology Clinic
Manhattan Specialty Care in the Press

Call now to make an appointment with our highly rated Manhattan Gynecology doctors regarding your health. We look forward to seeing you!
book online now
(212) 378-9985
New York City Locations:
Manhattan Women's Health & Wellness (Upper East Side)
983 Park Ave, Ste 1D17
New York, NY 10028
(212) 389-1904
Manhattan Women's Health & Wellness (Midtown)
56 W 45th St, Ste 815
New York, NY 10010
(212) 677-7654
Manhattan Women's Health & Wellness (Union Square)
55 W 17th St, Ste 104
New York, NY 10011
(212) 378-9985